Today I want to share about common medical devices used in emergency/ hospital and clinic setup. For medical students, you all may use this as your revision for your OSCE.
A) Oxygen Delivery Devices
1. Nasal Cannula

What?
-It is a disposable, plastic device with a two protruding prongs for insertion into nostrils, connected to an oxygen source.
Indication?
-used to deliver low flow oxygen
-patient is stable
Contraindication
-nasal blockage
-facial injuries
Advantages
-easily used
-safe and simple
-easily tolerated
Disadvantages
-unable to use with nasal obstruction
-drying to mucous membrane
-can dislodge from noses easily
-causes skin irritation or breakdown over ears.
2. Simple face mask
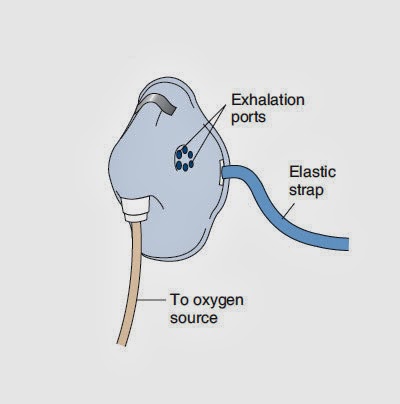
What?
-simple mask is made of clean, flexible, plastic or rubber that can be molded to fit the face.
Indication
-medium flow oxygen
-respiratory acidosis
Contraindication
-poor respiratory effort
-severe hypoxia
-apnea
Advantages
-can provide increased delivery of oxygen for short period of time.
Disadvantages
-tight seal required to deliver higher concentration
-difficult to keep mask in position over nose and mouth
-uncomfortable for patient while eating or talking.
3. Non-rebreathing face mask

Character
-two one-way valve
Indication
-delivery of high concentration of oxygen
-chronic airway limitation
Contraindication
-poor respiratory effort
-apnea
Advantages
-delivers the highest possible oxygen concentration
-suitable for patient breathing spontaneous with severe hypoxemia.
Disadvantages
-impractical for long term therapy
-expensive
-feeling of suffocation
-uncomfortable
4. Venturi mask
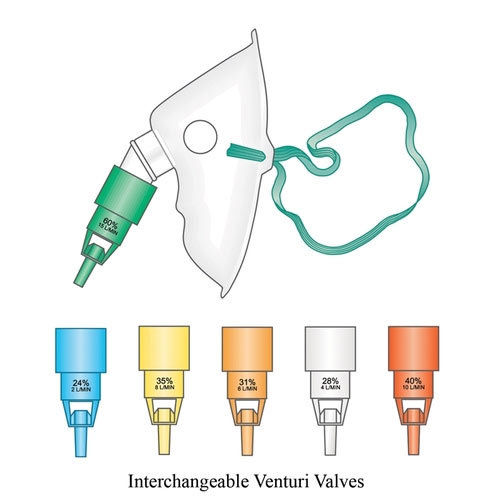
What?
-disposable face mask used to deliver a controlled oxygen concentration to patient.
-high flow oxygen mask.
-designed to allow inspired air to mix with oxygen.
Indication
-COPD
-Acute respiratory disease
Contraindication
-Poor respiratory efforts
-apnea
-severe hypoxia
Special precaution
-monitor SaO2 with pulse oximeter
-make sure the valve connected and function properly
-have risk of skin irritation.
5. Nebulizer mask

What?
-Is a drug delivery device used to administer medication in the form of a msit that is inhaled into the lungs.
Indication
-Administration of bronchodilators (salbutamol) in asthma and COPD
-Administration of corticosteroids such as (budesonide) in asthma patient
-Administration of mucolytic and antimicrobial in bronchiectasis and cystic fibrosis
-hypertonic saline to improve mucociliary clearance and lung function in patients with cystic fibrosis.
6. BVM Ventilator

Indication
-failure of ventilation or oxygenation
-failed intubation
Contraindication
-complete upper airway obstruction
-after induction
-after paralysis
Complication
-aspiration
-hypoventilation
7. Pulse oximeter

What?
-Is a non invasive method allowing the monitoring of oxygenation of patients hemoglobin.
Indication
-to monitor oxygen saturation in diseased states
-to monitor responsiveness to therapy
-to monitor side effect during procedures
-to detect blood flow in endagered body regions
Normal reading
-95% - 99%
Approach (technique)
-digit
-ears
-forehead
-palm / foot in neonates
A) Oxygen Delivery Devices
1. Nasal Cannula

What?
-It is a disposable, plastic device with a two protruding prongs for insertion into nostrils, connected to an oxygen source.
Indication?
-used to deliver low flow oxygen
-patient is stable
Contraindication
-nasal blockage
-facial injuries
Advantages
-easily used
-safe and simple
-easily tolerated
Disadvantages
-unable to use with nasal obstruction
-drying to mucous membrane
-can dislodge from noses easily
-causes skin irritation or breakdown over ears.
2. Simple face mask

What?
-simple mask is made of clean, flexible, plastic or rubber that can be molded to fit the face.
Indication
-medium flow oxygen
-respiratory acidosis
Contraindication
-poor respiratory effort
-severe hypoxia
-apnea
Advantages
-can provide increased delivery of oxygen for short period of time.
Disadvantages
-tight seal required to deliver higher concentration
-difficult to keep mask in position over nose and mouth
-uncomfortable for patient while eating or talking.
3. Non-rebreathing face mask
Character
-two one-way valve
Indication
-delivery of high concentration of oxygen
-chronic airway limitation
Contraindication
-poor respiratory effort
-apnea
Advantages
-delivers the highest possible oxygen concentration
-suitable for patient breathing spontaneous with severe hypoxemia.
Disadvantages
-impractical for long term therapy
-expensive
-feeling of suffocation
-uncomfortable
4. Venturi mask

What?
-disposable face mask used to deliver a controlled oxygen concentration to patient.
-high flow oxygen mask.
-designed to allow inspired air to mix with oxygen.
Indication
-COPD
-Acute respiratory disease
Contraindication
-Poor respiratory efforts
-apnea
-severe hypoxia
Special precaution
-monitor SaO2 with pulse oximeter
-make sure the valve connected and function properly
-have risk of skin irritation.
5. Nebulizer mask

What?
-Is a drug delivery device used to administer medication in the form of a msit that is inhaled into the lungs.
Indication
-Administration of bronchodilators (salbutamol) in asthma and COPD
-Administration of corticosteroids such as (budesonide) in asthma patient
-Administration of mucolytic and antimicrobial in bronchiectasis and cystic fibrosis
-hypertonic saline to improve mucociliary clearance and lung function in patients with cystic fibrosis.
6. BVM Ventilator

Indication
-failure of ventilation or oxygenation
-failed intubation
Contraindication
-complete upper airway obstruction
-after induction
-after paralysis
Complication
-aspiration
-hypoventilation
7. Pulse oximeter

What?
-Is a non invasive method allowing the monitoring of oxygenation of patients hemoglobin.
Indication
-to monitor oxygen saturation in diseased states
-to monitor responsiveness to therapy
-to monitor side effect during procedures
-to detect blood flow in endagered body regions
Normal reading
-95% - 99%
Approach (technique)
-digit
-ears
-forehead
-palm / foot in neonates